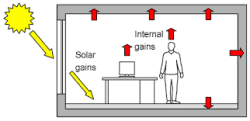
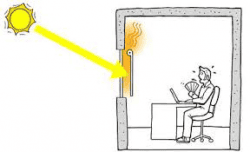
Solar heat gain is simply the heat accumulation in an object, structure or space due to the absorption of incident solar radiation by its surface. The level of solar heat accumulation that a space experiences is primarily a function of its ability to absorb and re-radiate solar radiation and the total incident light intensity experienced by the space. A greater incident light intensity means that more solar heat is absorbed; this heat accumulation can be measured in terms of absolute temperature, relative humidity (RH), ground temperature and other parameters.
Heat gain can take several forms. Some of these forms are known as conductive heat exchange, convective heat transport, radiant heat transport and enthalpy. All these forms occur because of certain properties of the solar cells themselves such as light sensitivity and the ability to absorb and re-radiate heat. The absorption of heat usually occurs in conduction or convective processes. To keep your building cool, consider Brise Soleil from Alu Systems
The third type of heat gain that is important is radiation convection. This occurs in objects where heat convection is the dominant mechanism for transporting heat from one region to another. Heat convection typically occurs in metal surfaces like stainless steel, aluminium, copper, titanium, tin, zinc, brass, bronze, iron etc. Where the surface has a high porosity like those found in metalloids, quartz, gemstones etc the heat conduction is enhanced and becomes more efficient.